Electrochemically induced reversible formation of carboxymethyl chitin hydrogel and tunable protein release†
Abstract
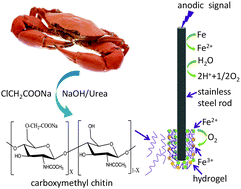
Carboxymethyl chitin is one of the most important derivatives of chitin that has been widely used in the fields of biomedicine and environmental treatment. In this contribution, carboxymethyl chitin was homogenously synthesized in NaOH–urea aqueous solution for the first time. The product was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and a titration method. Carboxymethyl chitin showed water solubility and cationic sensitivity. Reversible sol–gel transition could be performed by sequentially adding cations and a reducing agent. Further, we demonstrated that the reversible sol–gel transition of carboxymethyl chitin could be controlled on the surface of a stainless steel electrode by using an electrochemical method. Once an anodic signal was imposed to the electrode, sol–gel transition occurred due to the crosslinking of carboxymethyl chitin with Fe2+/Fe3+. The gel formation can be facilely controlled by voltage, concentration of carboxymethyl chitin and deposition time. Protein could be entrapped in the hydrogel simultaneously during the in situ formation of hydrogel. Protein release accelerated when a cathodic signal was imposed due to the electrochemically induced conversion of Fe2+/Fe3+ to Fe. The present result represents a “green” and simple process to synthesize carboxymethyl chitin and the prepared chitin derivative may have potential applications in electrochemically controlled drug delivery systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...