Promising ceria–samaria-based nano-oxides for low temperature soot oxidation: a combined study of structure–activity properties†
Abstract
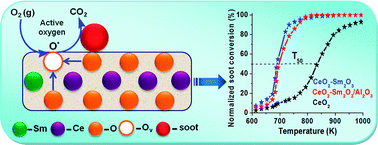
The design of promising heterogeneous catalysts is an urgent task for protecting the environment from automotive exhaust pollutants. In this work, the catalytic efficiency of nanosized Ce–Sm and Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 samples synthesized using economical coprecipitation and deposition coprecipitation methods, respectively, was investigated for diesel soot oxidation. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized materials were systematically analyzed by means of XRD, BET surface area, Raman spectroscopy, TG-DTA, FT-IR spectroscopy, HRTEM, ICP-OES, XPS, and UV-vis DRS techniques. XRD studies confirmed the formation of nanocrystalline single-phase Ce–Sm oxide solid solutions. HRTEM images showed the presence of small-sized nanocrystals (∼4–15 nm) in the synthesized samples. The Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 sample exhibited remarkable thermal stability compared with the Ce–Sm oxide and CeO2 samples, as evidenced by an insignificant variation in the crystallite size and BET surface area with high temperature thermal treatments. Owing to the disparity in the oxidation state of Sm3+ and Ce4+, abundant oxygen vacancies were formed in both the Ce–Sm and Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 samples. Interestingly, the oxygen vacancy concentration substantially decreased with increased calcination temperature, attributed to the high level of order of the samples. The catalytic activity results revealed that both the Ce–Sm and Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 samples show excellent soot oxidation performance compared with pristine CeO2 due to the presence of abundant oxygen vacancies and superior BET surface area. A 50% soot conversion was achieved at ∼690, 697 and 835 K with the Ce–Sm, Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 and CeO2 samples calcined at 773 K, respectively. It was found that the soot oxidation efficiency of the Ce–Sm and Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 samples strongly depends on the calcination temperature. Despite its trivial activity difference with respect to the Ce–Sm sample, the outstanding thermal stability of the Ce–Sm/γ-Al2O3 sample is vital in view of the practical working conditions of diesel engines.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...