Electrospun poly(l-lactide) nanofibers loaded with paclitaxel and water-soluble fullerenes for drug delivery and bioimaging†
Abstract
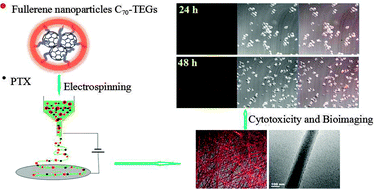
Multifunctional electrospun composite nanofibrous scaffolds have attracted much interest as drug delivery vehicles and in bioimaging application for real-time tracing the whole process of postoperative therapy. Novel poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) composite nanofibers loaded with water-soluble fullerene C70 nanoparticles and paclitaxel were successfully fabricated. The nanofibers with the average diameter of fibers ranging from 350 to 750 nm were uniform and their surfaces were reasonably smooth. The nanofibers showed an excellent hydrophilic surface and good mechanical properties. The in vitro release results demonstrated that the release rate of paclitaxel could be controlled by the content of C70 nanoparticles. With the increase of the content of C70 nanoparticles, the drug release rate became faster with increased total release amount. The composite nanofibers used as substrates for cytotoxicity and bioimaging in vitro were evaluated with human liver carcinoma HepG-2 cells. Paclitaxel was released from the composite nanofibers without losing cytotoxicity, the drug-loaded composite nanofibers inhibited the proliferation of HepG-2 cells effectively. Meanwhile, the fluorescent signal of C70 nanoparticles could be detected in HepG-2 cells, which reflected the growth state of cells clearly. These results strongly suggested that these PLLA composite nanofibers could be used in the fields of tissue engineering, drug delivery and bioimaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...