Amplified impedimetric DNA sensor based on graphene oxide–phenylboronic acid for sensitive detection of bleomycins
Abstract
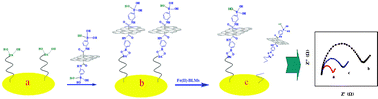
Due to the significance of bleomycins (BLMs) for the treatment of a variety of cancers, it is highly desirable to develop a sensitive method to quantitatively determine the BLMs content in both pharmaceutical analysis and clinical samples. Here, a simple, rapid, and convenient electrochemical method for BLMs detection was developed. Single-stranded DNA, as the substrate of BLMs, was self-assembled onto a gold electrode to fabricate an electrochemical DNA sensor, with one terminus tethered on the electrode surface and the other terminus labeled with graphene oxide–phenylboronic acid as a signal-amplification factor, giving a remarkable electron-transfer resistance (Ret). In the presence of Fe(II)·BLMs, the electrochemical DNA sensor undergoes an irreversible cleavage event, which can be transduced into a significant decrease in Ret. This sensor reveals a wide linear range from 0.05 nM to 1200 nM (R = 0.9869) and a low detection limit (0.01 nM, S/N = 3) for the determination of BLMs. It exhibits a good performance in a serum sample as well. Based on the high sensitivity and specificity of this electrochemical DNA sensor and the attractive characteristics of the electrochemical technique (cost effective and simple to implement), the developed impedimetric DNA sensor shows distinct advantages over conventional methods and is a promising alternative for the sensitive determination of BLMs in clinical samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...