Sensitive and selective colorimetric sensing of Fe3+ ion by using p-amino salicylic acid dithiocarbamate functionalized gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
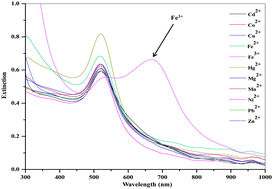
We have developed a selective and sensitive colorimetric method for determination of Fe3+ ion by using p-amino salicylic acid dithiocarbamate functionalized gold nanoparticles (DTC-PAS-Au NPs) as colorimetric probes. The DTC-PAS-Au NPs were characterized by FT-IR, 1H NMR, UV-visible spectrometry, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and atomic force microscopic (AFM) techniques, respectively. The DTC-PAS-Au NPs are aggregated rapidly by addition of Fe3+ ions, yielding a color change from red to blue. The characteristic surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak (520 nm) of DTC-PAS-Au NPs was shifted to longer wavelength, 700 nm, which confirms the ligand-to-metal charge transfer between DTC-PAS-Au NPs and Fe3+ ions. Under the optimal conditions, a good linear relationship (correlation coefficient R2 = 0.993) was obtained between the ratio of the extinction at 700 nm to that at 520 nm and the concentration of Fe3+ over the range of 40–80 μM, with a detection limit of 14.82 nM. The DTC-PAS-Au NPs acted as colorimetric sensors for the selective detection of Fe3+ ions in real samples (blood and urine samples).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...