A thermally and mechanically stable eco-friendly nanocomposite for chemical sensor applications†
Abstract
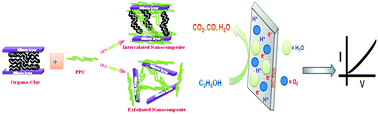
Ethanol chemical sensors have been developed by proficient exploitation of polypropylene carbonate (PPC) and PPC/cloisite 20B (clay) nanocomposite (NC) for the detection and quantification of ethanol in the environment. NC was synthesized by the addition of polypropylene carbonate (PPC) into 5 wt% of cloisite 20B. The physicochemical structure was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The thermal and mechanical properties of PPC and NC were investigated by thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and nanoindentation analyzer, respectively. NC displayed high thermal and mechanical properties. TGA results revealed that the thermal decomposition temperature (Td50%) of PPC increased significantly, being 43 °C higher than that of pure PPC, while DSC measurements indicated that NC increased the glass transition temperature from 21 to 32 °C. Accordingly, NC showed a high elastic modulus and hardness as compared to PPC. By applying to ethanol sensing, both PPC and NC performed as the best ethanol chemi-sensors in terms of sensitivity. NC showed 3.24 times higher sensitivity (0.8231 μA cm−2 mM−1) as compared to pure PCC (0.2543 μA cm−2 mM−1).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...