Some “remarkably stable” chalcogen(ii) dications, including comparisons with their structurally distinct monocations and neutrals
Abstract
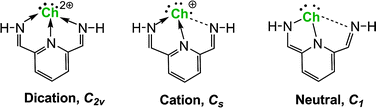
Ragogna and co-workers recently (2009 and thereafter) reported the syntheses and structures of a family of remarkably stable tridentate dications (Ch = S, Se and Te). We present a theoretical study of these fascinating compounds. For a better understanding of the extraordinary robustness of these dications, the analogous monocations and neutral species are also explored. The dications with C2v symmetries are genuine minima; for the monocations the equilibrium structures have Cs symmetry, with three distinct Ch–N distances; the neutral molecules have C1 symmetry, with one Ch–N bond effectively broken. Our theoretical results, including the natural charges, Wiberg bond indices (WBIs), and HOMO–LUMO gaps, provide reasonable explanations for their remarkable stability. The global minima of the monocations (with Cs symmetry) lie lower in energy than the corresponding C2v structures by 3.4, 1.1, and 0.3 kcal mol−1, respectively, for S, Se, and Te. The global minima of the neutrals (with C1 symmetry) lie lower in energy than their C2v structures by 23.7, 14.9, and 6.9 kcal mol−1 for the S, Se, and Te compounds, respectively. From our theoretical investigations, the viabilities for the dications, monocations, and the neutrals of these chalcogen(II) compounds fall in the order of S > Se > Te.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...