Detection of Cu(ii) and NO by ‘on–off’ aggregation in poly(aryl ether) dendron derivatives†
Abstract
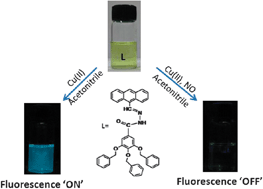
We report the detection of Cu(II) and NO at micro and nano-molar concentrations, respectively, by poly(aryl ether) dendron derivatives containing anthracene moiety attached through an acylhydrazone ‘molecular loop’. In the absence of Cu(II), the acylhydrazone moiety undergoes cis–trans photo-isomerization, resulting in negligible emission from

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...