P–C bond formation via direct and three-component conjugate addition catalyzed by ZnO nano-rods for the synthesis of 2-oxindolin-3-yl-phosphonates under solvent-free conditions
Abstract
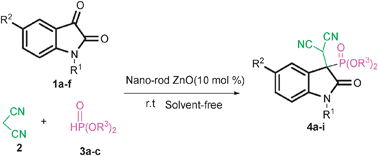
A simple and novel method is reported for the synthesis of 2-oxindolin-3-yl-phosphonates using ZnO nano-rods as a catalyst under solvent-free conditions at room temperature. ZnO nano-rods are synthesized successfully by employing Zn(OAc)2·2H2O, NH3 and polyethylene glycol (PEG , Mw = 2000). X-Ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and BET surface measurement were used to characterize the structure and morphology of the catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...