Potentiometric and multinuclear NMR investigations of di-/trimethyltin(iv) cations with some heterocyclic thiones in aqueous media
Abstract
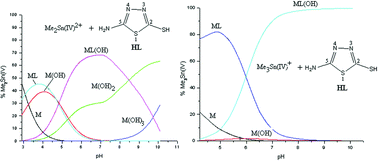
Equilibrium (pH-metric) studies of the interaction of Me2Sn(IV)2+ and Me3Sn(IV)+ with heterocyclic thiones, viz. 5-amino-3H-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione (HL-1), 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole-5-thione (HL-2) and 4-amino-3R-1,2,4-triazole-5-thione (where R = CH3 (HL-3) and C2H5 (HL-4)), in aqueous solution (I = 0.1 M KNO3, 298 K) were performed. The concentration distribution of the various complex species in solution was evaluated as a function of pH. It was found that these thione ligands (HL) with potential sulfur donor groups interact strongly with Me2Sn(IV)2+ and Me3Sn(IV)+, even at rather acidic pHs < 4.0. The species that exist at physiological pH (7.0) are Me2SnL(OH) (∼70–85%) and Me2Sn(OH)2 (∼15–30%) for dimethyltin(IV) systems, whereas Me3SnL(OH) (∼73–95%), Me3SnL (8–24%) and Me3Sn(OH) (∼1–3%) exist for Me3Sn(IV)+ systems. The complex species formed are water soluble in the pH range 2–10.5. In all of the studied systems, no polymeric species were detected in the experimental pH range. Beyond pH 8.0, significant amounts of hydroxo species, viz. Me3SnOH and Me2Sn(OH)2, were formed. Multinuclear (1H, 13C and 119Sn) NMR studies were also carried out at different pHs in order to characterize the possible geometry of the proposed complex species in aqueous solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...