Site-specific surface tailoring for metal ion selectivity via under-coordinated structure engineering†
Abstract
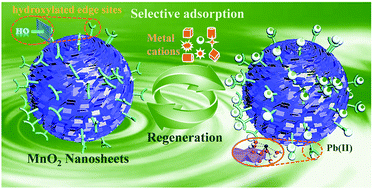
Coordinatively unsaturated atoms play an important role in structural and electronic tuning, while their effects on surface site tailoring for selective adsorption have not been well explored. We demonstrate a new concept based on elaborate tuning of the chemical states of lattice atoms to control the accessibility of different surface sites. The under-coordinated manganese structure developed herein not only benefits the formation of hydroxylated lateral edge sites for preferential complexation of lead (Pb) ions, but also favors a decrease in the proportions of metal-ion-nonspecific octahedral vacancy sites. On the basis of this strategy, a common core–shell structure was devised to further assemble highly exposed edge sites, achieving high selectivity coefficients (31.2–172.0) for Pb(II) against various metal cations. Even when these metal cations coexist at higher concentrations, the general specificity is still maintained, with further pH-enabled switchable sorption–desorption for adsorbent recyclability. Different from frequently reported specific ligand-induced selective systems, intrinsic structure modification as described herein will lead to a new paradigm for surface site tailoring that enables a versatile and tunable platform in environmental remediation, resource recovery and analyte sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...