Conjugated polyelectrolyte nano field emission adlayers†
Abstract
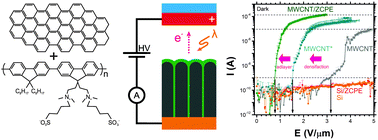
Here we report on a straightforward and rapid means of enhancing the field electron emission performance of nascent vertically aligned multi-walled carbon nanotubes by introducing a polar zwitterionic conjugated polyelectrolyte adlayer at the vacuum–emitter interface. We attribute the observed 66% decrease in turn-on electric field to the augmented emitter micro-morphology and shifted surface band structure. The composite emitters can be optically modulated by exploiting the absorption cross-section of the solution cast adlayer, which increases the local carrier concentration which broadens the effective electrostatic shape of the emitter during optical excitation. Assessment via scanning anode field emission microscopy reveals a 25% improvement in DC time stability, a significant reduction in long-term hysteresis shift, and a threefold increase in bandwidth during pulsed mode operation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...