Crossing the blood–brain barrier with carbon dots: uptake mechanism and in vivo cargo delivery†
Abstract
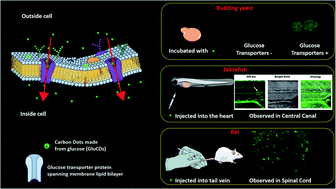
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a major obstacle for drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) such that most therapeutics lack efficacy against brain tumors or neurological disorders due to their inability to cross the BBB. Therefore, developing new drug delivery platforms to facilitate drug transport to the CNS and understanding their mechanism of transport are crucial for the efficacy of therapeutics. Here, we report (i) carbon dots prepared from glucose and conjugated to fluorescein (GluCD-F) cross the BBB in zebrafish and rats without the need of an additional targeting ligand and (ii) uptake mechanism of GluCDs is glucose transporter-dependent in budding yeast. Glucose transporter-negative strain of yeast showed undetectable GluCD accumulation unlike the glucose transporter-positive yeast, suggesting glucose-transporter-dependent GluCD uptake. We tested GluCDs' ability to cross the BBB using both zebrafish and rat models. Following the injection to the heart, wild-type zebrafish showed GluCD-F accumulation in the central canal consistent with the transport of GluCD-F across the BBB. In rats, following intravenous administration, GluCD-F was observed in the CNS. GluCD-F was localized in the gray matter (e.g. ventral horn, dorsal horn, and middle grey) of the cervical spinal cord consistent with neuronal accumulation. Therefore, neuron targeting GluCDs hold tremendous potential as a drug delivery platform in neurodegenerative disease, traumatic injury, and malignancies of the CNS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...