Multi-stimuli responsive heterotypic hydrogels based on nucleolipids show selective dye adsorption†
Abstract
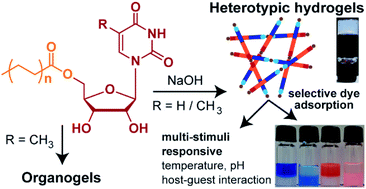
Analogous to nucleic acids, the building blocks of nucleic acids and their derivatives are widely used to create supramolecular architectures for application mainly in the field of biomedicine. Here, we describe the construction of a multi-stimuli responsive and toxic dye adsorbing heterotypic hydrogel system formed using simple nucleoside–fatty acid conjugates. The nucleolipids are derived by coupling fatty acid chains of different lengths at the 5′ position of ribothymidine and uridine. The nucleolipids in the presence of a strong base (e.g. NaOH) undergo partial hydrolysis, which triggers the self-assembly of the hydrolysed components resulting in the formation of heterotypic hydrogels. Notably, the gels are formed specifically in the presence of Na+ ions as other ions such as Li+ and K+ did not support the hydrogelation process. Systematic analysis by microscopy, NMR, single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction and rheology indicated that the deprotonated nucleolipid and fatty acid salt interdigitate and provide necessary electrostatic interactions supported by Na+ ions to set the path for the hierarchical assembly process. Notably, the hydrogels are highly sensitive to external stimuli, wherein gel–sol transition can be reversibly controlled by using temperature, pH and host–guest interaction. One of the hydrogels made of 5′-O-myristate-conjugated ribothymidine was found to selectively adsorb cationic dyes such as methylene blue and rhodamine 6G in a recyclable fashion. Taken together, the easily scalable assembly, multi-stimuli responsiveness and ability to capture and release dyes highlight the potential of our nucleolipid hydrogel system in material applications and in the treatment of dye industry wastes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...