A convenient detection system consisting of efficient Au@PtRu nanozymes and alcohol oxidase for highly sensitive alcohol biosensing†
Abstract
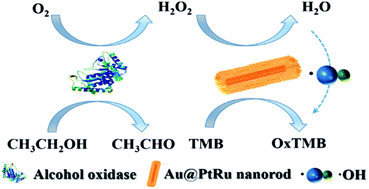
Effective alcohol detection represents a substantial concern not only in the context of personal and automobile safety but also in clinical settings as alcohol is a contributing factor in a wide range of health complications including various types of liver cirrhoses, strokes, and cardiovascular diseases. Recently, many kinds of nanomaterials with enzyme-like properties have been widely used as biosensors. Herein, we have developed a convenient detection method that combines Au@PtRu nanozymes and alcohol oxidase (AOx). We found that the Au@PtRu nanorods exhibited peroxidase-like catalytic activity that was much higher than the catalytic activities of the Au and Au@Pt nanorods. The Au@PtRu nanorod-catalyzed generation of hydroxyl radicals in the presence of H2O2 was used to develop an alcohol sensor by monitoring the H2O2 formed by the oxidation of alcohol to acetaldehyde in the presence of AOx. When coupled with AOx, alcohol was detected down to 23.8 μM in a buffer solution for biological assays. Notably, alcohol was successfully detected in mouse blood samples with results comparable to that from commercial alcohol meters. These results highlight the potential of the Au@PtRu nanorods with peroxidase-like activity for alcohol detection, which opens up a new avenue for nanozyme development for biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...