Controlling wettability, wet strength, and fluid transport selectivity of nanopaper with atomic layer deposited (ALD) sub-nanometer metal oxide coatings†
Abstract
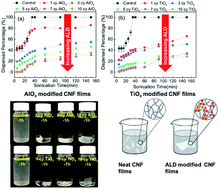
Nanocellulosic films (nanopapers) are of interest for packaging, printing, chemical diagnostics, flexible electronics and separation membranes. These nanopaper products often require chemical modification to enhance functionality. Most chemical modification is achieved via wet chemistry methods that can be tedious and energy intensive due to post-processing drying. Here, we discuss the use of atomic layer deposition (ALD), a vapor phase modification technique, to quickly and simply make nanopaper hydrophobic and enhance its wet strength and durability. Specifically, we find that just “a few” ALD cycles (≤10) of either aluminum oxide or titanium oxide is sufficient to significantly increase the durability of cellulose nanofibril (CNF) paper in aqueous media, even under aggressive sonication conditions. Keeping the number of ALD cycles low makes the process more scalable for commodity manufacturing. We investigate whether this increase in wet strength is due to enhanced hydrophobic attractions or stronger hydrogen bonding between CNF fibers. The current evidence suggests that the latter mechanism is likely dominant, with ab initio calculations suggesting that newly created M–OH terminations on the cellulose nanofibrils increase hydrogen bond strength between fibers and impede CNF hydration and dispersion. ALD treated nanopapers are also found to preferentially transport hexane over water, suggesting their potential use in oil/water demulsification devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...