Ultra-small Rh nanoparticles supported on WO3−x nanowires as efficient catalysts for visible-light-enhanced hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane†
Abstract
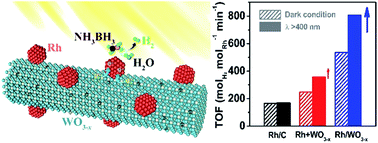
Hydrolysis of ammonia borane (AB) is a safe and convenient means of H2 production when efficient catalysts are used. Here we report a facile one-pot solvothermal method to synthesize Rh/WO3−x hybrid nanowires. Ultra-small Rh nanoparticles with an average size of ∼1.7 nm were tightly anchored on WO3−x nanowires. Rh/WO3−x catalysts exhibited substantially enhanced activity for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB under both dark and visible light irradiation conditions relative to mixed Rh nanoparticles and WO3−x nanowires (Rh + WO3−x), and Rh/C and WO3−x nanowires. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis indicated that the synergistic effect between Rh nanoparticles and WO3−x nanowires was responsible for such an enhancement in activity. Specifically, Rh/WO3−x achieved the highest turnover frequency (TOF) with a value of 805.0 molH2 molRh−1 min−1 at room temperature under visible light irradiation. The H2 release rate as a function of reaction time exhibited a volcano plot under visible light irradiation, indicating that a self-activation process occurred in the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB due to additional oxygen vacancies arising from in situ reduction of WO3−x nanowires by AB, and thus an enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). Such a self-activation process was responsible for the enhanced catalytic activity under visible light irradiation relative to that under dark conditions, which was supported by the lower activation energy (45.2 vs. 50.5 kJ mol−1). In addition, Rh/WO3−x catalysts were relatively stable with only little loss in activity after five cycles due to the tight attachment between two components.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...