Substrate-independent and catalyst-free synthesis of magnesium nanowires†
Abstract
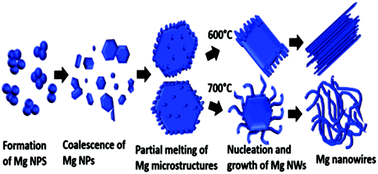
We report a catalyst free and substrate independent synthesis of magnesium nanowires using a simple thermal evaporation method. The produced Mg nanowires have a size of 8–60 nm with a crystalline MgO shell of ∼2–5 nm thickness. The synthesized nanowires grow along the [001] direction and horizontal to the substrate. Moreover, from ex situ TEM investigation the various sequential stages involved in the nanowire formation process were identified. The experimental outcome indicates the sequential stages including (i) formation of Mg nanoparticles, (ii) coarsening of Mg nanoparticles to microparticles via deposition diffusion aggregation (DDA) and the orientation attachment (OA) process, and (iii) nucleation and growth of Mg nanowires. In depth analysis confirms two types of nanowires, straight and serpentine-like, where the latter dominates as the holding duration/temperature of the synthesis increases. The straight nanowires are formed by the direct attachment of nanodroplets from the core to the surface and serpentine-like wires are formed on the surface of a microparticle which is in a quasi-melted state. Moreover, nanowires were produced by confining the Mg vapour to the substrate using a curved quartz bottle, thereby controlling the supersaturation in the absence of any inert/reactive gas during the synthesis. Our synthesis method is cost effective and can be applied to other low melting point elements for producing various nanostructures. Finally based on the experimental results a possible growth mechanism is proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...