Compound-specific adaptation of hepatoma cell lines to toxic iron†
Abstract
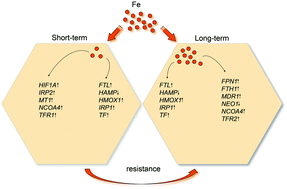
Cellular adaptation to excess iron (Fe) is a major determinant to protect tissues from toxicity. The adaptation of hepatoma cell lines following exposure to toxic levels of Fe compounds was studied. A dose- and time-dependent induction of toxicity was observed that was strictly compound-specific. Similar ranging orders of toxicity, i.e. iron chloride >iron sulfate >iron citrate, were observed in four human hepatoma cell lines. Long-term cultivation of HepG2 cells in 10 mM iron citrate resulted in a resistant cell line that displayed high proliferation rates for several months. Resistant cells showed increased viability at iron citrate concentrations ranging from 5–15 mM, while exposition to iron chloride or iron sulfate induced high rates of toxicity similar to parental cells. Resistance was not due to decreased Fe uptake/storage since high intracellular Fe levels were observed. A broad range of modulated gene expression was associated with short- and long-term iron citrate exposition; however, after weaning of resistant cells, re-exposition to Fe induced a similar level of toxicity as observed in parental cells suggesting that a transient adaptation of gene expression was mounted. The results indicate that, depending on the nature of the Fe compound, a specific level of toxicity is induced in hepatic cells which however can be overcome by establishment of resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...