Elemental bioimaging of manganese uptake in C. elegans
Abstract
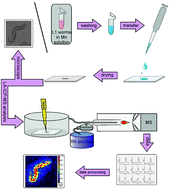
A new method for elemental bioimaging with laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) was developed and applied to study the uptake of manganese (Mn) in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). C. elegans is a well-established model organism in neuroscience, genetics and genomics, which has been extensively studied to decipher mechanisms of heavy metal induced toxicity. Knowledge about the distribution of manganese (Mn) and other metals in this organism will be helpful in elucidating pathways and mechanisms of transport, distribution and excretion. The LA-ICP-MS method requires limited sample preparation and can be used rapidly and easily to visualize the Mn distribution in C. elegans. Due to thorough optimization of the analytical parameters, intense Mn signals in C. elegans wild-type (WT) and mutants were obtained at a spatial resolution as small as 4 μm, thus proving the suitability of LA-ICP-MS to study the uptake of metals in C. elegans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...