Anisotropic tough multilayer hydrogels with programmable orientation†
Abstract
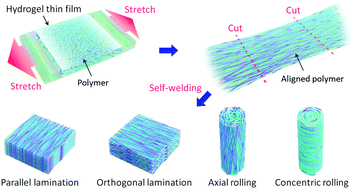
Hydrogels are normally isotropic and weak, in contrast to their natural analogs that possess hierarchically oriented structure and excellent mechanical properties. Inspired by the unique structure of natural materials, we develop an approach for preparing highly anisotropic hydrogels with programmable oriented polymer structure and extraordinary mechanical properties. Our method is based on a novel welding technique for stretched cellulose hydrogel films, in which interfacial reconfiguration occurs, allowing full integration without compromising the highly aligned polymer orientation. We demonstrate the versatility of this method by fabricating four types of anisotropic tough multilayer hydrogels with differently oriented hierarchies: parallel lamination (‖), orthogonal lamination (⊥), axial rolling, and concentric rolling. These high-water-content hydrogels (∼68 wt%) exhibit extremely high anisotropy (birefringence ≥0.006, the highest reported for hydrogels) and superior mechanical properties (Young's modulus of ∼140 MPa, tensile strength of ∼47 MPa, and work of extension of ∼20 MJ m−3). Moreover, these hydrogels also show interesting anisotropic electrical conductivity and asymmetric shape deformation. Because this method is easy to apply and offers flexibility in designing complex hierarchical hydrogel structures, our work opens a new window to designing novel hydrogel materials for engineering and biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...