Magnetically tunable organic semiconductors with superparamagnetic nanoparticles†
Abstract
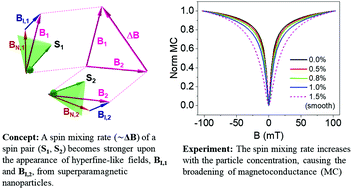
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) exhibiting superparamagnetic properties might generate large magnetic dipole–dipole interaction with electron spins in organic semiconductors (OSECs). This concept could be considered analogous to the effect of hyperfine interaction (HFI). In order to investigate this hypothesis, Fe3O4 MNPs are used as a dopant for generating random hyperfine-like magnetic fields in a HFI-dominant π-conjugated polymer host, poly(2-methoxy-5-(2-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylenevinylene) (MeH-PPV). The magnetoconductance (MC) response in organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) made by MeH-PPV/MNP blends is used to estimate the effective hyperfine field in the blends. Firstly, we find that the shape of the MC response essentially remains the same regardless of the MNP concentration, which is attributed to the similar functionality between the nuclear spins and magnetic moments of the MNPs. Secondly, the width of the MC response increases with increasing MNP concentration. Magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) experiments and micromagnetic simulation indicate that the additional increase of the MC width is associated with the magnetization of the blend. Finally, the MC broadening has the same temperature dependent trend as the magnetization of the MNPs where the unique effect of the MNPs in their superparamagnetic and ferromagnetic regimes on the MC response is observed. Magneto-photoinduced absorption (MPA) spectroscopy confirms that the MC broadening is not due to defects introduced by the MNPs but a result of their unique superparamagnetic behavior. Our study yields a new pathway for tuning OSECs’ magnetic functionality, which is essential for organic optoelectronic devices and magnetic sensor applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
