Study of segmental dynamics and ion transport in polymer–ceramic composite electrolytes by quasi-elastic neutron scattering†
Abstract
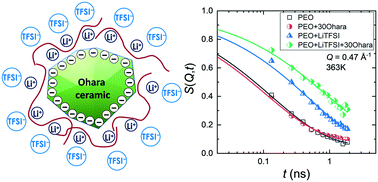
Composite electrolytes composed of a polymer electrolyte and an ion-conducting ceramic are promising in fulfilling the requirements for a stable lithium metal anode. In this work, we identify the effects of the surface of a lithium-ion-conducting ceramic, the Ohara LICGC™ ceramic, on the segmental dynamics and ionic conductivity of polymer electrolyte consisting of poly(ethylene oxide) and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI). Using quasi-elastic neutron scattering, we study the segmental motion of PEO chains under the confinement of LiTFSI salt and Ohara ceramic, in to the melt state (363 K). We compare the relaxation time, τ, and the monomeric friction coefficient, ζ, of four samples: neat PEO, PEO + Ohara ceramic, PEO + LiTFSI and PEO + LiTFSI + Ohara ceramic. In the absence of LiTFSI, Ohara ceramic posed negligible change in the segmental dynamics of PEO. In contrast, with the presence of LiTFSI, Ohara ceramic slowed down the segmental motion of PEO chains by ∼60% compared to neat PEO + LiTFSI. The intrinsic ionic conductivity of the polymer phase in the composite decreased by ∼30% compared to the neat polymer electrolyte. The underpinnings of these results may be that polymer chains in the vicinity of the ceramic surface are less mobile due to coordination with surface bound lithium ions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Charge Transporting Nanostructured Polymers for Electrochemical Systems


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...