Overcoming synthetic challenges in targeting coenzyme A biosynthesis with the antimicrobial natural product CJ-15,801†
Abstract
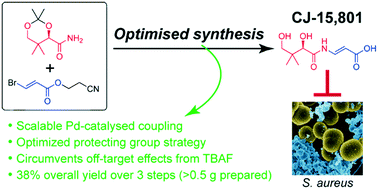
The biosynthesis of the essential metabolic cofactor coenzyme A (CoA) has been receiving increasing attention as a new target that shows potential to counter the rising resistance to established antimicrobials. In particular, phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase (PPCS)—the second CoA biosynthesis enzyme that is found as part of the bifunctional CoaBC protein in bacteria, but is monofunctional in eukaryotes—has been validated as a target through extensive genetic knockdown studies in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Moreover, it has been identified as the molecular target of the fungal natural product CJ-15,801 that shows selective activity against Staphylococcus aureus and the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. As such, CJ-15,801 and 4′-phospho-CJ-15,801 (its metabolically active form) are excellent tool compounds for use in the development of new antimicrobial PPCS inhibitors. Unfortunately, further study and analysis of CJ-15,801 is currently being hampered by several unique challenges posed by its synthesis. In this study we describe how these challenges were overcome by using a robust palladium-catalyzed coupling to form the key N-acyl vinylogous carbamate moiety with retention of stereochemistry, and by extensive investigation of protecting groups suited to the labile functional group combinations contained in this molecule. We also demonstrate that using TBAF for deprotection causes undesired off-target effects related to the presence of residual tertiary ammonium salts. Finally, we provide a new method for the chemoenzymatic preparation of 4′-phospho-CJ-15,801 on multi-milligram scale, after showing that chemical synthesis of the molecule is not practical. Taken together, the results of this study advances our pursuit to discover new antimicrobials that specifically target CoA biosynthesis and/or utilization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...