Anti-cancer effect of a novel 2,3-didithiocarbamate-substituted naphthoquinone as a tumor metabolic suppressor in vitro and in vivo†
Abstract
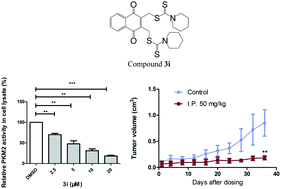
Tumor cells reprogram their cellular metabolism by switching from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis to support aberrant cell proliferation. Suppressing tumor cell metabolism has become an attractive strategy for treating cancer patients. In this study, we identified a 2,3-didithiocarbamate-substituted naphthoquinone 3i that inhibited the proliferation of tumor cells by disturbing their metabolism. Compound 3i reduced cancer cell viability with IC50 values from 50 nM to 150 nM against HCT116, MCF7, MDA-MB231, HeLa, H1299 and B16 cells. Further, compound 3i was found to suppress ATP production in cultured cancer cells, inhibit the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2) which is a rate-limiting enzyme in the glycolytic pathway and block the subsequent transcription of the downstream genes GLUT1, LDH and CCND1. In addition, exposure to compound 3i significantly suppressed tumor growth in a B16 melanoma transplantation mouse model and a spontaneous breast carcinoma mouse model in vivo. The identification of compound 3i as a tumor metabolic suppressor not only offers a candidate compound for cancer therapy, but also provides a tool for an in-depth study of tumor metabolism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...