MAO inhibitory activity of bromo-2-phenylbenzofurans: synthesis, in vitro study, and docking calculations†
Abstract
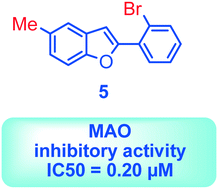
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is an enzyme responsible for metabolism of monoamine neurotransmitters which play an important role in brain development and function. This enzyme exists in two isoforms, and it has been demonstrated that MAO-B activity, but not MAO-A activity, increases with aging. MAO inhibitors show clinical value because besides the monoamine level regulation they reduce the formation of by-products of the MAO catalytic cycle, which are toxic to the brain. A series of 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives was designed, synthesized and evaluated against hMAO-A and hMAO-B enzymes. A bromine substituent was introduced in the 2-phenyl ring, whereas position 5 or 7 of the benzofuran moiety was substituted with a methyl group. Most of the tested compounds inhibited preferentially MAO-B in a reversible manner, with IC50 values in the low micro or nanomolar range. The 2-(2′-bromophenyl)-5-methylbenzofuran (5) was the most active compound identified (IC50 = 0.20 μM). In addition, none of the studied compounds showed cytotoxic activity against the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Molecular docking simulations were used to explain the observed hMAO-B structure–activity relationship for this type of compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...