Abstract
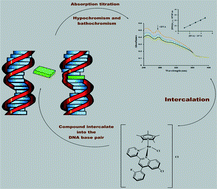
A series of substituted quinoline derivatives were synthesized via the Friedländer condensation reaction, using substituted 2-aminobenzophenone with 2-acetyl pyridine or 2-acetyl thiophene in the presence of sodium methoxide. The series of substituted quinoline based organometallic ruthenium complexes of the type [(Cp*)Ru(Ln)Cl]·Cl (where, Cp* = the pentamethylcyclopentadienyl ring, Ln = L1–7 = quinoline ligands) were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, electronic spectra, conductance measurements, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and mass spectrometry. They are known as piano stool complexes, due to the similarity of their structures to a piano stool, and the metal centre is coordinated by a pentamethylcyclopentadienyl ring, chlorido ligand and chelating quinoline ligand. All the compounds were investigated for their in vitro antimicrobial activity against five different bacterial strains, and their interaction with herring sperm (HS) DNA; absorption titration (Kb = 0.34–6.25 × 105 L mol−1) and viscosity measurements were also carried out. From the studies, we conclude that the complexes display the classical intercalative mode of DNA binding. The DNA-binding properties of all the compounds were also examined theoretically, using a molecular docking study, which proved the intercalation binding mode between compounds and nucleotide base pairs of HS DNA. The capability of the compounds to cleave pUC19 DNA was examined by chemical nuclease activity. The results indicate that the ruthenium complexes promote the cleavage of plasmid DNA more effectively than the respective quinoline ligands. All the compounds were evaluated for cytotoxicity activity against S. pombe cells at the cellular level and exhibited enhanced activity against S. pombe cells, compared to the quinoline ligands. All synthesized compounds were also evaluated for their in vitro antimalarial activity [50% inhibition concentration (IC50) = 0.55–1.84 mg L−1] against the Plasmodium falciparum strain, as well as in vitro cytotoxic activity [50% lethal concentration (LC50) = 5.64–119.67 mg L−1] against brine shrimp (Artemia cysts) eggs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...