Intrinsic reactivity profile of electrophilic moieties to guide covalent drug design: N-α-acetyl-l-lysine as an amine nucleophile†
Abstract
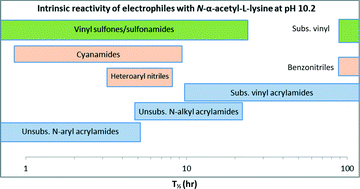
Covalent drugs contain a reactive electrophilic moiety or covalent reactive group (CRG), which forms an irreversible bond between the drug and a biological target. Consequently, the intrinsic reactivity of the CRG is an important consideration in the design of irreversible inhibitors. Although reactivity assessments of CRGs with sulfur nucleophiles, such as glutathione and cysteine have been reported, reactivity of these moieties with amine-containing nucleophiles is not well described. In this study, intrinsic reactivities were determined for a series of electrophiles (acrylamides, nitriles, cyanamides, sulfones, and sulfonamides) using N-α-acetyl-L-lysine as a model amine-based nucleophile and compared with results using glutathione (GSH). Since the ε-amine of N-α-acetyl-L-lysine is protonated at neutral pH, reactions were carried out at pH 10.2. In addition to reporting rate data for reactions of CRGs with N-α-acetyl-L-lysine, elements of selectivity relative to thiol-containing nucleophiles are also be discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...