Fluorinated thiazolidinols cause cell death in A549 lung cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK/ERK signalling pathways†‡
Abstract
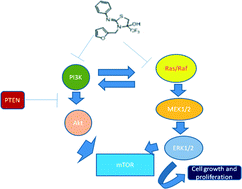
A series of 2-imino-4-(trifluoromethyl)thiazolidin-4-ol derivatives were synthesized from one pot, three-component reactions of primary amine, aryl isothiocyanate and 3-bromo-trifluoromethyl acetone via in situ generation of both symmetrical and unsymmetrical thioureas. All the synthesized derivatives were screened for their in vitro anti-cancer activity against human cancer cell lines. Compounds 8l, 8r, 8s, 8t and 8u exhibited more potent anticancer activity in lung cancer cells (A549) than in the other three cell lines. Data obtained from analysis of the cell cycle showed that treatment of lung cancer cells with these compounds resulted in G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Studies to understand the molecular mechanism of action of these compounds suggest that the compounds inhibit PI3K, pAkt and mTOR protein expression with concomitant up-regulation of tumor suppressor PTEN. These compounds contributed to LC-3 mediated cytoplasmic vacuolation leading to cell death in lung cancer cells. Overall, these compounds modulate cell death processes via inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways, the key growth factor signalling pathways implicated in abnormal cell proliferation. These molecules can therefore be further tested in in vivo models as a potential regimen for efficacy and effectivity in lung cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...