Design, synthesis and in vivo evaluation of sodium 2-benzyl-chloromalonates as new central nervous system depressants†
Abstract
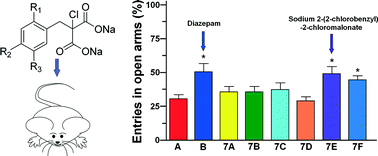
This work describes the design, synthesis and in vivo evaluation of new central nervous system depressing agents that show low levels of acute toxicity as well as high solubility in water and exhibit anxiolytic and hypnotic effects. These new compounds are sodium 2-benzyl-2-chloromalonates, which were designed using molecular modelling techniques and synthesized in four steps, with an overall yield between 41% and 65%. In vivo tests with mice, including pentobarbital-induced sleep, rotarod, open field and elevated plus maze tests, were carried out, and the results indicated that some of these agents induce activities similar to those induced by diazepam but with lower hypnotic potency and greater anxiolytic potency. These compounds were also orally administered to mice in doses of 2 g kg−1, and their effects were evaluated for 14 days. The mice did not show signs of intoxication, confirming that sodium 2-benzyl-2-chloromalonates exhibit low levels of acute toxicity. These observations indicate that sodium 2-benzyl-2-chloromalonates and their analogues are efficient and safer central nervous system depressing drugs relative to existing standards of care.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...