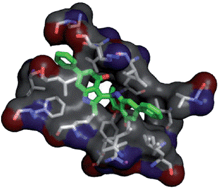
Progression through the S phase of the cell cycle is controlled by cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), the activity of which depends on its binding to regulatory partners (cyclins E and A). Deregulation of the activity of CDK2 has been associated with several types of sickness, such as infectious, neurodegenerative, and proliferative diseases. Based on these data, CDK2 has become an attractive target for the development of new anticancer drugs. Indoledione derivatives have recently received special attention in virtue of their pronounced biological effects, such as antiproliferative, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. In the present work we have investigated the antiproliferative effect of an indolone-based derivative, namely DPIT, whose synthesis we have recently reported, with the aim to clarify its mechanism of action. Furthermore, docking studies have been performed on the eight stereoisomers of DPIT to investigate their capacity to interact as a ligand with ortho- or allosteric sites of CDK2. The encouraging results showed DPIT as a promising candidate for a new type 3 class of inhibitors of CDK2 that recognize the allosteric site.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...