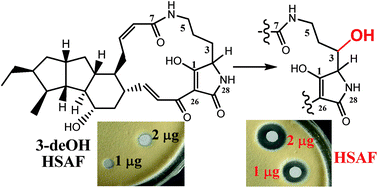
HSAF isolated from Lysobacter enzymogenes is an antifungal natural product with a new mode of action. The polycyclic tetramate macrolactam (PTM) carries a 3-hydroxyl group on the ornithine residue, which is a feature common to nearly all PTM type natural products found in phylogenetically diverse organisms. A previous gene disruption experiment indicated that the sterol desaturase (SD) gene, which is clustered with the central polyketide synthase–nonribosomal peptide synthetase (PKS–NRPS), was involved in the 3-hydroxylation. However, the mechanism for this hydroxylation had not been established. Here, we determined the structure of the main metabolite accumulated in the SD mutant, which is 3-dehydroxy HSAF (3-deOH-HSAF). This compound lost the antifungal activity against Penicillium avellaneum, showing the crucial role of the 3-hydroxyl group. We then expressed the SD gene in E. coli. Upon feeding 3-deOH-HSAF, E. coli produced HSAF. When the SD enzyme extract was incubated with 3-deOH-HSAF in the presence of NADPH, HSAF was also produced. The results demonstrated that the SD gene encodes a 3-hydroxylase of the HSAF carbon chain. In addition, the data support that the 3-hydroxylation step is likely a post-PKS–NRPS event in the HSAF biosynthetic pathway. Finally, we co-expressed the ferredoxin reductase (FNR) gene, which is also clustered with the PKS–NRPS gene, with the SD gene in E. coli. The results showed that FNR significantly enhanced the conversion of 3-deOH-HSAF into HSAF. Together, the study established the mechanism for the installation of this common functionality that is important to the activity of the PTM-type natural products.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...