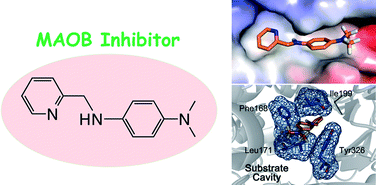
The design of multifunctional, neuroprotective compounds has received increasing attention due to their perceived utility in targeting not only the diverse comorbidity of neurological disorders, but also the typically complex pathoetiological pathways leading to these disorders, including insoluble proteins associated with many human neurodegenerative diseases of aging and radical-generating enzyme actions in the brain. For this purpose, herein, we present inhibitory studies on monoamine oxidase (MAO) of a chemical library composed of stilbene-like derivatives that have potential applications in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), with the ability to modulate metal-induced amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation and neurotoxicity in vitro and in living cells. Two isoforms of MAO, MAOA and MAOB, are well-known drug targets for depression and Parkinson's disease (PD), respectively. Interestingly, inhibition and binding affinity studies of MAO with our chemical series indicated that three compounds, L1-b, L2-b, and L3-b, exhibited potent and relatively selective inhibitory effects of MAOB. In particular, L2-b was observed to be the most effective MAOB inhibitor in our chemical library showing a reversible and competitive inhibition. Generally, compounds having a dimethylamino moiety in our chemical family showed greater MAO inhibition suggesting a structure–activity relationship. Overall, our findings demonstrate that the stilbene-like scaffolds could be utilized for developing promising multifunctional, neuroprotective agents for several neurodegenerative diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...