Modeling of alcohol oxidase enzyme of Candida boidinii and in silico analysis of competitive binding of proton ionophores and FAD with enzyme†
Abstract
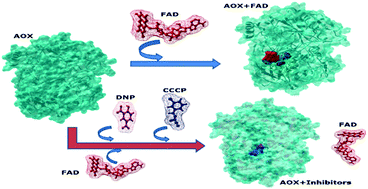
Alcohol oxidase (AOX) is an important flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) dependent oxidoreductase, which is responsible for converting methanol into formaldehyde and hydrogen peroxide for the growth of methylotrophic yeast Candida boidinii. Although AOX plays a crucial role in methanol catabolism, the experimental structure of AOX from Candida boidinii has not been elucidated. This study reports the first complete in silico model of AOX from C. boidinii. This paper also reports the AOX structure modeled using the threading approach, followed by structure analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. The modeled structure was compared with the aryl alcohol oxidase structure (a glucose–methanol–choline family member, pdbID: 3fim). A docking study was performed to analyze the interaction between AOX and its cofactor FAD. The AOX modeled structure also exhibited high similarity with respect to the FAD binding sites, which are the substrate binding sites as seen with 3fim. It was observed that the adenosine part of FAD was deeply buried inside AOX while the isoalloxazine ring stuck to the surface. This paper reports the interaction of selective proton ionophores (CCCP and DNP) with AOX and also reports their binding sites. These proton ionophores showed competitive binding with FAD. The occupancy of the FAD binding sites by the proton ionophore may lead to blocking of the entry of FAD and thereby disruption of AOX import into peroxisomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...