Super RLuc8-sFv; a new luciferase-labeled probe for detection of human CD4+ cells†
Abstract
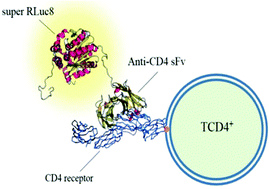
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) destroys CD4+ lymphocytes and monitoring these cells is one of the best techniques for studying HIV infection. In the present study a novel bioluminescent probe, super RLuc8-sFv, is developed in order to detect human CD4+ cells by fusion of an anti-human CD4 sFv to the C-terminus of super RLuc8. The results indicate that the probe can bind to CD4+ cells via its sFv domain; also it emits visible light through its signalling domain. Super RLuc8-sFv provides a new gateway for detection of human CD4+ cells using luminometric-based assays and may reduce the difficulties involved in, and the cost of, HIV-related diagnostic tests.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...