HOTTIP: a critical oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers
Abstract
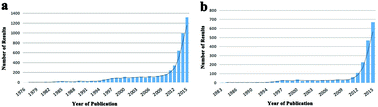
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which represent a novel group of non-protein-coding RNAs and are commonly defined as RNA molecules larger than 200 nucleotides in length, have been shown to get involved in diverse biological processes, such as cell growth, apoptosis, migration and invasion. In addition, aberrant expression of lncRNAs has been discovered in human tumors, where they function as either oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. Recently tumorigenic effects of one specific lncRNA, termed as ‘HOXA transcript at the distal tip’ (HOTTIP), on the initiation and progression of human cancer has been widely reported. An increasing amount of data has shown that dysregulation of HOTTIP is associated with various malignancies including hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer, and affects the survival and prognosis of cancer patients. Here, we focus on the current knowledge of HOTTIP in various cancers and illustrate the corresponding mechanism and biological function of HOTTIP during tumor development.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...