Comparative effects of dexamethasone and bergenin on chronic bronchitis and their anti-inflammatory mechanisms based on NMR metabolomics
Abstract
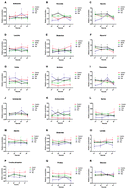
In order to compare the effect of dexamethasone and bergenin on chronic bronchitis and to reveal their anti-inflammatory mechanisms, 1H NMR-based metabolomics was performed to explore the potential biomarkers of the disease and study the therapeutic mechanisms of the drugs. In this study, 40 Sprague-Dawley male rats were randomly divided into 4 groups, namely control, model, dexamethasone and bergenin groups, with 10 rats in each group. Except for the control group, rats from the other three groups were exposed to tobacco smoke for 1 h d−1 for 28 days. During the modeling, dexamethasone (0.2 mg kg−1) and bergenin (87 mg kg−1) were administered orally to dexamethasone or bergenin rats 3 h after exposure every day. On the other hand, control and model rats were intragastrically administered water. According to the results of morphometric analysis of the airway epithelium and the count of white blood cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), dexamethasone and bergenin could suppress the infiltration of inflammatory cells, inhibit the secretion of mucus, and reduce white blood cells in BALF. Serum samples from the rats' orbits were collected every week. The metabolic profiles of sera were analyzed by multivariate statistical analyses, including PCA, PLS-DA and OPLS-DA models, and 18 metabolites were identified. The dynamic fluctuations of these biomarkers in sera from different groups were detected. The results suggested that the anti-inflammatory mechanism of dexamethasone may be associated with BCAA metabolism and glycolysis while bergenin could change BCAA metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, and glycolysis to treat chronic bronchitis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...