Structure-based virtual screening and experimental validation of the discovery of inhibitors targeted towards the human coronavirus nucleocapsid protein†
Abstract
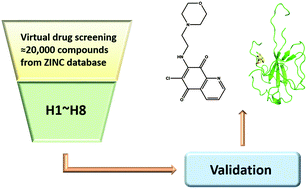
Nucleocapsid protein (NP), an essential RNA-binding viral protein in human coronavirus (CoV)-infected cells, is required for the replication and transcription of viral RNA. Recent studies suggested that human CoV NP is a valid target for antiviral drug development. Based on this aspect, structure-based virtual screening targeting nucleocapsid protein (NP) was performed to identify good chemical starting points for medicinal chemistry. The present study utilized structure-based virtual screening against human CoV-OC43 using the Zinc database, which is performed through docking with varying precisions and computational intensities to identify eight potential compounds. The chosen potential leads were further validated experimentally using biophysical means. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis indicated that one among the potential leads, 6-chloro-7-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethylamino) quinoxaline-5,8-dione (small-compound H3), exhibited a significant decrease of RNA-binding capacity of NP by more than 20%. The loss of binding activity was manifested as a 20% decrease in the minimum on-rate accompanied with a 70% increase in the maximum off-rate. Fluorescence titration and X-ray crystallography studies indicated that H3 antagonizes the binding between HCoV-OC43 NP and RNA by interacting with the N-terminal domain of the NP. Our findings provide insight into the development of new therapeutics that disrupt the interaction between RNA and viral NP in the HCoV. The discovery of the new compound would be an impetus to design novel NP inhibitors against human CoV.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Coronavirus articles - free to access collection and Chemical Biology in Molecular BioSystems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...