Analysis of urinary metabolomic profiling for unstable angina pectoris disease based on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy†
Abstract
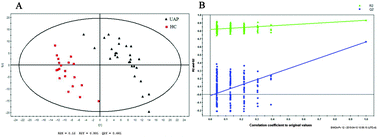
1H NMR-based urinary metabolic profiling is used for investigating the unstable angina pectoris (UAP) metabolic signatures, in order to find out candidate biomarkers to facilitate medical diagnosis. In this work, 27 urine samples from UAP patients and 20 healthy controls were used. The metabolic profiles of the samples were analyzed by multivariate statistics analysis, including PCA, PLS-DA and OPLS-DA. The PCA analysis exhibited slight separation with R2X of 0.681 and Q2 of 0.251, while the PLS-DA (R2X = 0.121, R2Y = 0.931, and Q2 = 0.661) and the OPLS-DA (R2X = 0.121, R2Y = 0.931, Q2 = 0.653) demonstrated that the model showed good performance. By OPLS-DA, 20 metabolites were identified. A diagnostic model was further constructed using the receiver–operator characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC = 0.953), which exhibited a satisfying sensitivity of 92.6%, specificity of 90% and accuracy of 89.1%. The results demonstrated that the NMR-based metabolomics approach showed good performance in identifying diagnostic urinary biomarkers, providing new insights into the metabolic process related to UAP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...