Thermodynamic characterization of the interaction between the human Y-box binding protein YB-1 and nucleic acids†
Abstract
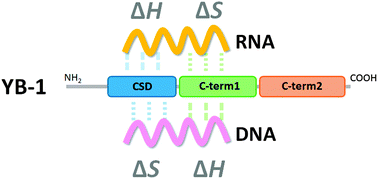
Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) binds to both RNA and DNA to control transcription and translation for the regulation of various cellular systems. YB-1 is overexpressed in some cancer cells and is a potential target for treatment of cancer. Herein, we describe isothermal titration calorimetry analyses of the interaction between a number of recombinant YB-1 domains and nucleic acids to identify the RNA and DNA binding sites and their binding mechanisms. These results demonstrated that the C-terminal domain of the protein interacts with single-stranded DNA and RNA by exothermic and endothermic reactions, respectively. The highly conserved cold-shock domain (CSD) also bound to single-stranded RNA and DNA by exothermic and endothermic reactions, respectively. The specific binding manner for RNA is in the CSD, whereas DNA binds with the most affinity to the C-terminal region (amino acids 130–219). We found further that the C-terminal region (amino acids 220–324) regulates the binding stoichiometry of RNA. These quantitative thermodynamic results provide a preliminary indication on the molecular mechanism of binding of the multifunctional protein YB-1 to nucleic acids to regulate its biological function.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...