Fuzzy modeling reveals a dynamic self-sustaining network of the GLI transcription factors controlling important metabolic regulators in adult mouse hepatocytes†
Abstract
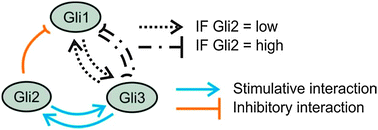
The GLI transcription factors, GLI1, GLI2, and GLI3, transduce Hedgehog and non-hedgehog signals and are involved in regulating development and tumorgenesis. Surprisingly, they were recently found to modulate important functions of mature liver. However, less is known about their mutual interactions and possible target genes in mature hepatocytes. To get a deeper insight into these interactions cultured mouse hepatocytes were transfected with siRNAs against each GLI factor. RNA was extracted at different times and the expression levels of the genes of interest were determined by quantitative real-time PCR. The time-dependent data were analysed by a fuzzy logic-based modelling approach. The results indicated that the GLI factors constitute an interconnected network. GLI2 inhibited GLI1 expression and was coupled with GLI3 by a positive feedback loop. The regulatory activity between GLI1 and GLI3 was more complex switching between a positive and a negative feedback loop depending on whether the level of GLI2 is low or high, respectively. Generally, this network structure enables a dynamic behaviour. When GLI2 is low, it may keep GLI1 and GLI3 activity balanced favouring the appropriate modulation of transcription factors like the Ppars and Srebp1. When GLI2 is high, it may prevent an uncontrolled amplification that may lead to cancer. In conclusion, the three GLI factors in mature hepatocytes form an interactive transcriptional network that is involved in the control of target genes associated with metabolic zonation as well as with lipid and drug metabolism. Its structure in mature cells seems different from embryonic cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...