Characterization of disulfide bonds by planned digestion and tandem mass spectrometry†
Abstract
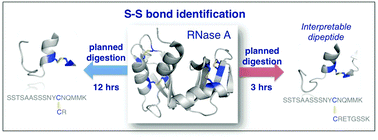
The identification of disulfide bonds provides critical information regarding the structure and function of a protein and is a key aspect in understanding signaling cascades in biological systems. Recent proteomic approaches using digestion enzymes have facilitated the characterization of disulfide-bonds and/or oxidized products from cysteine residues, although these methods have limitations in the application of MS/MS. For example, protein digestion to obtain the native form of disulfide bonds results in short lengths of amino acids, which can cause ambiguous MS/MS analysis due to false positive identifications. In this study we propose a new approach, termed planned digestion, to obtain sufficient amino acid lengths after cleavage for proteomic approaches. Application of the DBond software to planned digestion of specific proteins accurately identified disulfide-linked peptides. RNase A was used as a model protein in this study because the disulfide bonds of this protein have been well characterized. Application of this approach to peptides digested with Asp-N/C (chemical digestion) and trypsin under acid hydrolysis conditions identified the four native disulfide bonds of RNase A. Missed cleavages introduced by trypsin treatment for only 3 hours generated sufficient lengths of amino acids for identification of the disulfide bonds. Analysis using MS/MS successfully showed additional fragmentation patterns that are cleavage products of S–S and C–S bonds of disulfide-linkage peptides. These fragmentation patterns generate thioaldehydes, persulfide, and dehydroalanine. This approach of planned digestion with missed cleavages using the DBond algorithm could be applied to other proteins to determine their disulfide linkage and the oxidation patterns of cysteine residues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...