Proteomic analysis of rhein-induced cyt: ER stress mediates cell death in breast cancer cells†
Abstract
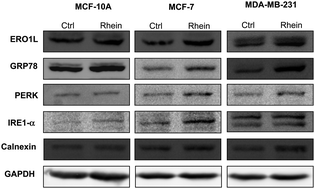
Rhein is a natural product purified from herbal plants such as Rheum palmatum, which has been shown to have anti-angiogenesis and anti-tumor metastasis properties. However, the biological effects of rhein on the behavior of breast cancers are not completely elucidated. To evaluate whether rhein might be useful in the treatment of breast cancer and its cytotoxic mechanism, we analyzed the impact of rhein treatment on differential protein expression as well as redox regulation in a non-invasive breast cancer cell line, MCF-7, and an invasive breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-231, using lysine- and cysteine-labeling two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) combined with MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. This proteomic study revealed that 73 proteins were significantly changed in protein expression; while 9 proteins were significantly altered in thiol reactivity in both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The results also demonstrated that rhein-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells mostly involves dysregulation of cytoskeleton regulation, protein folding, the glycolysis pathway and transcription control. A further study also indicated that rhein promotes misfolding of cellular proteins as well as unbalancing of the cellular redox status leading to ER-stress. Our work shows that the current proteomic strategy offers a high-through-put platform to study the molecular mechanisms of rhein-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. The identified differentially expressed proteins might be further evaluated as potential targets in breast cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...