N-Formyl-7-amino-11-cycloamphilectene, a marine sponge metabolite, binds to tubulin and modulates microtubule depolymerization†
Abstract
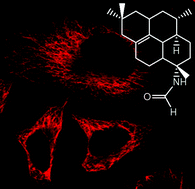
The importance of protein–small molecule interaction in drug discovery, medicinal chemistry and biology has driven the development of new analytical methods to disclose the whole interactome of bioactive compounds. To accelerate targets discovery of N-formyl-7-amino-11-cycloamphilectene (CALe), a marine bioactive diterpene isolated from the Vanuatu sponge Axinella sp., a chemoproteomic-based approach has been successfully developed. CALe is a potent anti-inflammatory agent, modulating NO and prostaglandin E2 overproduction by dual inhibition of the enhanced inducible NO synthase expression and cyclo-oxygenase-2 activity, without any evidence of cytotoxic effects. In this paper, several isoforms of tubulin have been identified as CALe off-targets by chemical proteomics combined with bio-physical orthogonal approaches. In the following biological analysis of its cellular effect, CALe was found to protect microtubules against the colcemid depolymerizing effect.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...