Site selectivity for protein tyrosine nitration: insights from features of structure and topological network†
Abstract
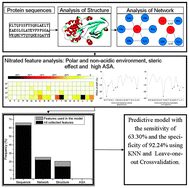
Tyrosine nitration is a covalent post-translational modification, which regulates protein functions such as hindering tyrosine phosphorylation and affecting essential signal transductions in cells. Based on up-to-date proteomics data, tyrosine nitration appears to be a highly selective process since not all tyrosine residues in proteins or all proteins are nitrated in vivo. Quite a few investigations included the protein structural information from the RCSB PDB database, where near 100 000 high-quality three-dimensional structures are available. In this work, we analyzed the local protein structures and amino acid topological networks of the nitrated and non-nitrated tyrosine sites in nitrated proteins, including neighboring atomic distribution, amino acid pair (AAP) and amino acid triangle (AAT). It has been found that aromatic and aliphatic residues, particularly with large volume, aromatic, aliphatic, or acidic side chains, are disfavored for the nitration. After integrating these structural features and topological network features with traditional sequence features, the predictive model achieves a sensitivity of 63.30% and a specificity of 92.24%, resulting in a much better accuracy compared to the previous models with only protein sequence information. Our investigation implies that the site selectivity may stem from a more open, hydrophilic and high-pH chemical environment around the tyrosine residue.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...