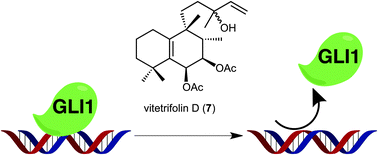
The hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway has crucial roles in embryonic development, cell maintenance and proliferation, and is also known to contribute to cancer cell growth. New naturally occurring Hh inhibitors (1, 7 and 9) were isolated from Vitex negundo using our previously constructed cell-based assay. Bioactivity guided isolation provided 9 natural compounds including a new diterpene, nishindanol (9). Compounds 7 and 9 showed cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines in which Hh signaling was aberrantly activated. Vitetrifolin D (7; GLI1 transcriptional inhibition IC50 = 20.2 μM) showed inhibition of Hh related protein (PTCH and BCL2) production. Interestingly, the constructed electrophoresis mobility shift assay revealed that vitetrifolin D (7) disrupted GLI1 binding on its DNA binding domain. epi-Sclareol (8; inactive), possessing a similar structure to 7, did not show inhibition of GLI1–DNA complex formation. This is the first example of naturally occurring inhibitors of GLI1–DNA complex formation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...