Metabolite target analysis of human urine combined with pattern recognition techniques for the study of symptomatic gout
Abstract
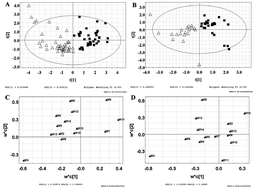
Recurrent attacks and irregularity are two important characteristics of gout disease. Uric acid as a single evaluation indicator for clinical diagnosis is insufficient considering the versatile properties of gout. The aim of this work is to identify several endogenous metabolites from urine samples for the elucidation and prediction of gout disease. Metabolite target analysis was established for human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection (HPLC-DAD). The targeted metabolites selected included hippuric acid, uracil, phenylalanine, tryptophan, uric acid and creatinine as well as nine purine compounds. Useful information was extracted from multivariate data through Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis (FDA) and Orthogonal Signal Correction Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OSC-PLS-DA). Uric acid, hypoxanthine, xanthosine, guanosine, inosine and tryptophan were identified as important metabolites among the acute and chronic gout and controls. Based on OSC-PLS-DA models, the regression equations obtained could discriminate gout from the controls as well as the acute from chronic. The recognition and prediction ability is respectively 100% and 85.0% for the gout, 100% and 83.3% for the acute, and 90.91% and 89.9% for the chronic. Metabolic dysfunction of tryptophan and excessive metabolism of xanthosine and hypoxanthine to xanthine were confirmed for gout disease. Metabolic dysfunction of tryptophan was also proven to be induced by allopurinol in case of Kunming mice with hyperuricemia. Potential biomarkers can be used not only to distinguish gout patients from healthy people, but also to evaluate the disease state.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...