Computational prediction and analysis of protein γ-carboxylation sites based on a random forest method†
Abstract
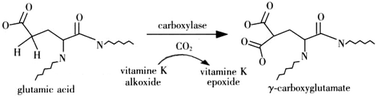
The glutamate γ-carboxylation plays a pivotal part in a number of important human diseases. However, traditional protein γ-carboxylation site detection by experimental approaches are often laborious and time-consuming. In this study, we initiated an attempt for the computational prediction of protein γ-carboxylation sites. We developed a new method for predicting the γ-carboxylation sites based on a Random Forest method. As a result, 90.44% accuracy and 0.7739 MCC value were obtained for the training dataset, and 89.83% accuracy and 0.7448 MCC value for the testing dataset. Our method considered several features including sequence conservation, residual disorder, secondary structures, solvent accessibility, physicochemical/biochemical properties and amino acid occurrence frequencies. By means of the feature selection algorithm, an optimal set of 327 features were selected; these features were considered as the ones that contributed significantly to the prediction of protein γ-carboxylation sites. Analysis of the optimal feature set indicated several important factors in determining the γ-carboxylation and a possible consensus sequence of the γ-carboxylation recognition site (γ-CRS) was suggested. These may shed some light on the in-depth understanding of the mechanisms of γ-carboxylation, providing guidelines for experimental validation.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...