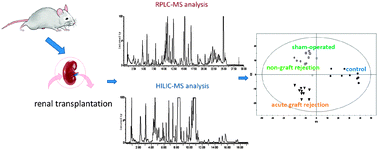
Acute graft rejection is one of the most common and serious post complications in renal transplantation, noninvasive diagnosis of acute graft rejection is essential for reducing risk of surgery and timely treatment. In this study, a non-targeted metabonomics approach based on ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MS) is used to investigate the effect of acute graft rejection in rat renal transplantation on metabolism. To collect more metabolite information both hydrophilic interaction chromatography and reversed-phase liquid chromatography were used. Using the partial least squares-discriminant analysis, we found that the change of metabonome in a sham-operated group and a non-graft rejection group had a similar trend, while that of the acute graft rejection group was clearly different. Several discriminating metabolites of the acute graft rejection were identified, including creatinine, phosphatidyl-cholines, lyso-phosphatidylcholines, carnitine C16:0, free fatty acids and indoxyl sulfateetc. These discriminating metabolites suggested that acute graft rejection in renal transplantation can lead to the accumulation of creatinine in the body, and also the abnormal metabolism of phospholipids. These findings are useful to understand the mechanisms of the rejection, it also means that a UPLC-MS metabonomic approach is a suitable tool to investigate the metabolic abnormality in the acute graft rejection in renal transplantation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...