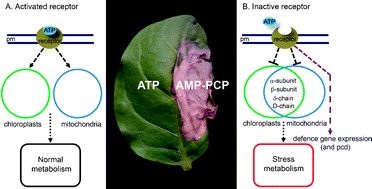
Complex signalling systems have evolved in multicellular organisms to enable cell-to-cell communication during growth and development. In plants, cell communicationvia the extracellular matrix (apoplast) controls many processes vital for plant survival. Secretion of ATP into the extracellular matrix is now recognised as a previously unknown stimulus for cell signalling with a role in many aspects of plant physiology. In the last decade, the secondary messenger molecules in extracellularATP signalling were identified, but the downstream gene and protein networks that underpin plant responses to extracellular ATP are only beginning to be characterised. Here we review the current status of our knowledge of plant extracellular signalling and demonstrate how applying state-of-the art proteomic technologies is rapidly bringing new discoveries in extracellular ATP research. We discuss how monitoring of the global proteomic profile during responses to modulation of extracellularATP signalling has led to novel insight into pathogen defence systems and plant programmed cell death regulation. On the basis of extensive proteomic, pharmacological, and reverse genetics data, extracellular ATP has been confirmed to constitute an important molecular switch that tightly controls organellar energy metabolism, reprogramming of primary metabolic pathways, and redirection of resources to protein networks that support adaptation of plants to stress.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...